Polypharmacy Risks: How Taking Too Many Medications Can Hurt You
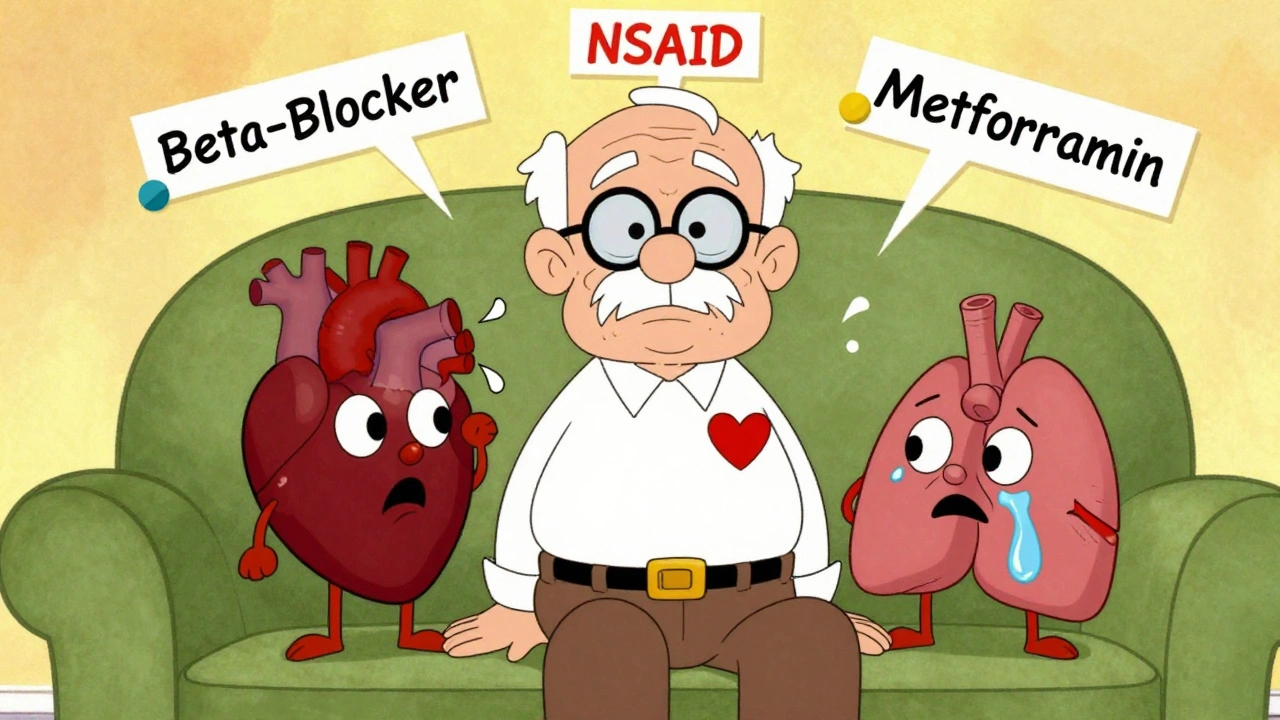
When you're taking polypharmacy, the use of multiple medications by a single patient, often for different conditions. Also known as multiple medication use, it's common in older adults and people with chronic illnesses—but it's not harmless. Every extra pill you swallow adds a new chance for something to go wrong. It’s not just about side effects—it’s about how those drugs talk to each other inside your body.
Think of your body like a busy kitchen. Add one spice, fine. Add ten, and suddenly your dish is ruined. That’s what happens with drug interactions, when two or more medications react in a way that changes their effect. For example, mixing SSRIs with certain painkillers can trigger serotonin syndrome, a life-threatening spike in brain chemicals. Or combining blood thinners with anti-inflammatories can turn a minor cut into a serious bleed. These aren’t rare edge cases—they show up in real patients every day, and they’re often missed because doctors focus on one condition at a time.
And it’s not just the drugs themselves. medication safety, the practice of using drugs correctly to avoid harm gets messy when you’re juggling ten different bottles, each with its own schedule, warnings, and refill rules. People forget doses. They double up because they’re not sure if they already took it. They mix generics and brands without knowing the difference. One study found that nearly half of adults over 65 who take five or more meds make at least one dangerous error each month. That’s not carelessness—it’s a system failure.
What makes this worse is that many of these meds aren’t even necessary. Some are prescribed for symptoms that could be managed differently. Others are kept on file just because no one ever reviewed them. A polypharmacy checklist isn’t about cutting pills—it’s about asking: Is this still helping? Could this be replaced? Is there a safer way?
You’ll find posts here that show you exactly how these risks play out in real life. From how insulin and blood pressure drugs can clash, to why stacking pain meds with sleep aids is riskier than you think, to how pharmacist substitution rules might accidentally swap a safe drug for a dangerous one. You’ll see how people manage refills while traveling, how to read labels so you don’t accidentally overdose, and what to ask your doctor before adding another pill to your routine. This isn’t theory. These are stories from people who’ve been there—and the clear steps they took to get back in control.